Introduction
Do you know in rural areas, WPR (Worker Population Ratio) increased from 44.8% in 2017-2018 to 54.2% in 2022-2023?
The significance of skill development in India can be cited as one of the most important factors for job creation. India has a unique advantage in demographic terms as more than 60% of its population can be considered young. However, in order to leverage this huge workforce, employability needs to be enhanced.
The GDP of India is expanding at a rate of 6-8% but job creation is not keeping up. Compared to its neighbours, India can be considered a relatively young country. Around 28 million young people enter the Indian workforce each year.
Although the government of India has formulated several plans for the development of skills, these plans have not yielded the desired results in terms of creating opportunities for skill development training in the Indian landscape. These goals include:
- Increasing proficiency
- Expansion of skill sets
- Completion of tasks in a shorter amount of time with more outcomes
- Increment in the level of performance
AISECT has collaborated with NSDC and has pioneered the Market-led Fee-based services scheme which can be considered a driving force in the establishment of a sustainable skill training ecosystem.
The Need for Skill Development in India
According to statistics, the WPR in urban areas increased from 42.6% in 2017-18 to 46% in 2022-23.
- • Supply and demand issues: On the supply side, India is continuously failing to create enough job opportunities while on the demand side, professionals entering the job market are lacking skill sets. This is resulting in rising unemployment rates along with low employability.
- • Rising unemployment: As per CMIE, the unemployment rate in India is around 7-8% in 2022 which has increased by 5% in the last five years. In addition to that the workforce shrank as thousands of people dejected over weak job prospects pulled out which is a situation that was exacerbated by the Covid 19 pandemic.
- • Lack of workforce skills: While keeping pace with the generation of employment is one issue, the productivity and employability of those entering the labour market is another issue.
- • Demand for skilled workforce: The CII (Confederation of Indian Industry) had projected an increase in HR requirement till 2022 at 201 million making the total requirement of the skilled workforce by 2023 at 300 million.
AISECT’s Vision and Mission
Do you know that only 10% of graduates in India can be considered employable?
Established in 1985, AISECT aims to bridge the digital divide between the semi-urban and rural masses while building a capable generation. Going into the future, AISECT aims to aspire to empower the next set of generations with the right skills, cultural identities and exposure. AISECT is transforming lives by skilling and upskilling, digitally enabling services for India, quality and affordable higher education, expanding reach of financial services, aiding in e-governance, and promoting Indian art and culture while connecting the youth employment, livelihood and entrepreneurship opportunities.
Key Components of AISECT’s Skill Mission
Did you know that 90% of the recent graduates lack the skills necessary for corporate employment?
AISECT has been continuously working in the field of skill development and training for the past 31 years. It has reached the remotest corners of the country. It can be considered a pioneer in impacting skill development courses in local languages which explains its reach at the grassroots.
AISECT’s reach within the country can be aptly showcased through a demographic pyramid in which the penetration of the activities of AISECT is highest at the bottom of the pyramid.
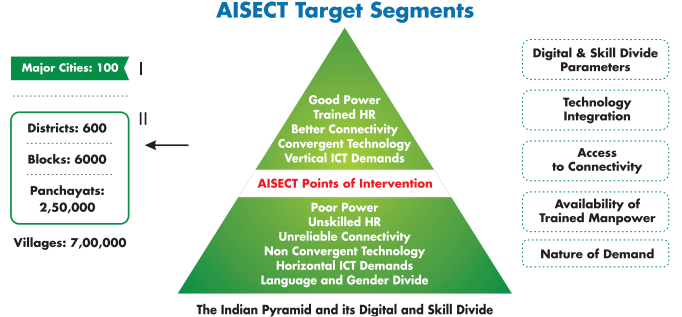
AISECT collaborated with NSDC with the mission to skill around 1.3 million youth across semi-urban and rural areas in 2012 in 7 out of 21 priority sectors identified by NSDC. The 7 sectors that are taken up by AISECT for youth training are IT and ITES, Hardware and Electronics, Teacher and Assessor training, Banking and Financial Services, Textiles, organized retail and Agri skills. These can be considered the sectors which are estimated to have the highest contribution towards skill-workforce requirement in the country over the next 10 years.
The main objectives of the partnerships are as follows:
- The expansion of skilling and training facilities of AISECT, first in the backward and rural areas of the states such as Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Jharkhand, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Odisha, Maharashtra, Punjab and then expand across the country.
- To undertake massive training of trainers program for the improvement of quality skill training and to upskill the technology utilization by trainers in various aspects of training.
- The utilization of approximately 6000 CSCs (Common Service Centers) established by AISECT at the Panchayat Level across MP, Chhattisgarh and Punjab for the purpose of skilling youth.
- To support the training programs related to skill development by the provision of placement services to both online and offline candidates or the trained manpower.
- To develop and expand the AISECT Content Creation Center as the spine or backbone of all ongoing skill development efforts by the organisation.
In addition to that, to complement initiatives like Skill India and Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan, aisectlearn.com was established as the largest free online open learning platform. AISECT is committed to revolutionizing education by providing comprehensive vocational training solutions to school students. The program is designed to equip students with practical skills that will prepare them for the challenges of the modern world. It has also established SGSU which is central India’s first NSQF and NEP-aligned skills university in Bhopal under the skilling initiative.
Conclusion
AISECT aims to bridge the digital divide between urban, semi-urban and rural areas by the provision of various services and facilities. Skill development, which can be considered a crucial proponent of economic growth and the reduction of the unemployment rate, is the need of the hour and AISECT is bridging the gaps related to skill development and employability.



